52 UK Experience of Non-Radioisotope, Non-Magnetic Guided Breast Wide Local Excision and Sentinel Node Biopsy
Background
The standard treatment for early breast cancer with node-negative axilla is wide local excision (WLE) and sentinel lymph node biopsy (SNB). Guide-wire WLE for impalpable cancers poses various challenges. The use of magnetic seeds has been adopted as an alternative solution. Difficult detectability, magnetic interference with metallic instruments/MRI, and recalibration remain open issues. The common technique for SNB is radioisotope with or without blue dye. The radioisotope poses various problems including handling and disposal of isotopes. The short half-life of the isotope restricts the scheduling of surgery and hinders patients’ flow into the operating theater. Finally, concerns have previously been raised regarding the efficacy of ICG in patients with high body mass index (BMI). We present our experience in WLE plus SNB using a non-wire, non-magnetic breast localization method plus non-radioisotope technique for sentinel node identification. A comparison with the magnetic breast localization method is provided. The aims of the study are:
- Compare oncological clearance of cancer between magnetic and nonmagnetic localization seeds.
- Demonstrate a good identification rate of SNB using a
non-radioisotope fluorescent dye. - Confirm good node detection rate with the ICG regardless of patients’ BMI.
Methods
Patient and Tumor Characteristics of Patients Having WLE With SAVI SCOUT and Magseed
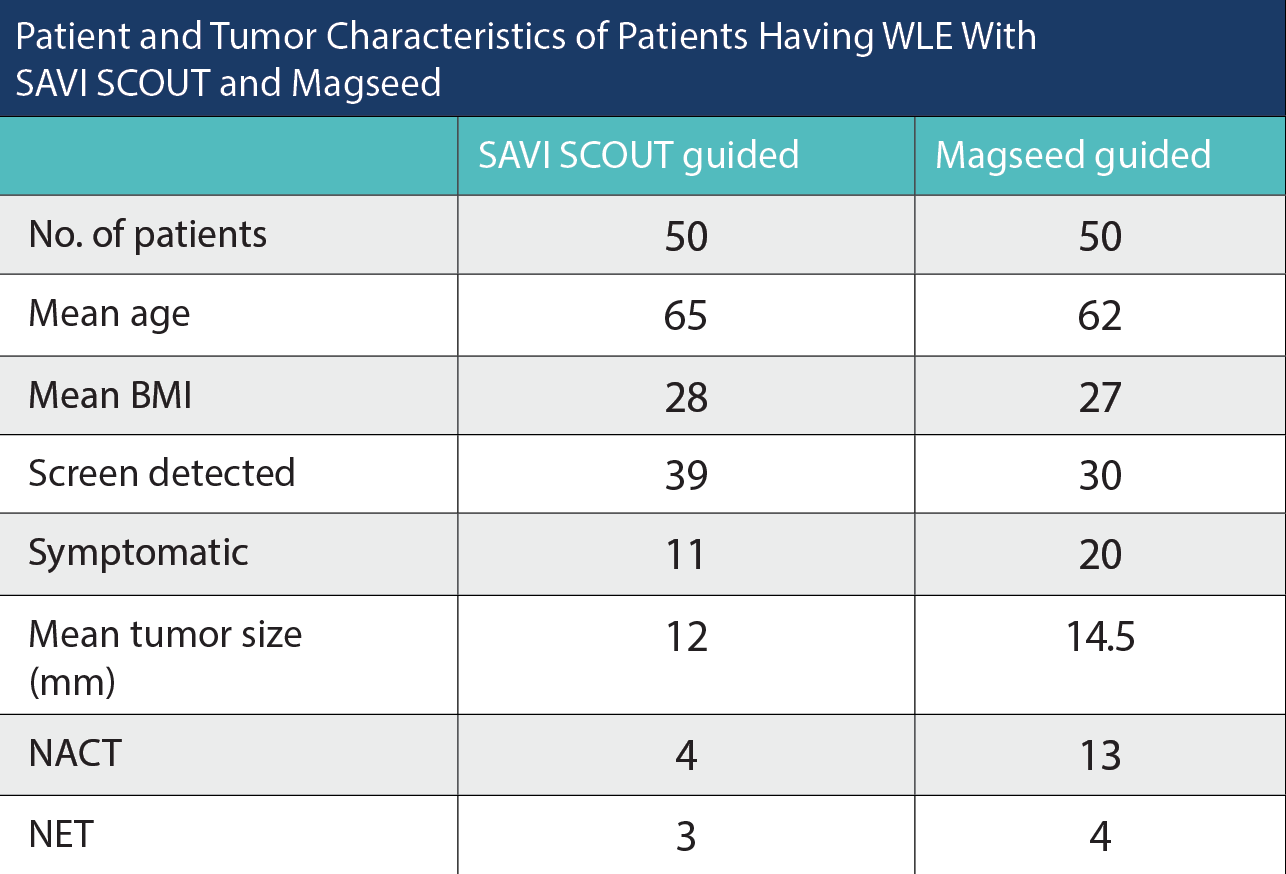
We compared 50 patients with WLE and SNB using SAVI SCOUT plus ICG with 50 cases using Magseed plus ICG in 2022/2023. The SAVI SCOUT clip was placed 1 to 5 days before surgery. Additionally, 2 mL of ICG and 2 mL of blue dye were injected intradermally in the periareolar area.
Results
The identification rate of SNB with ICG dye was 100% despite high BMI. Also, BMI has not affected the number of nodes retrieved (average number of SNB was 2, similar to other case series). A total of 5 of the patients localized with SAVI SCOUT had positive margins (10%) compared with 6 localized with magnetic seed (12%). The re-excision rate using SAVI SCOUT/Magseed is not statistically significant. Compared with guide wire, the use of SAVI SCOUT reduced the re-excision rate by 50% in our case series (15% vs 10%).
Conclusions
Non-magnetic localization of impalpable breast cancers showed a good detection rate with adequate margins clearance (10% re-excision rate, compared with 17.2% UK average). The use of ICG in SNB (with blue dye) is associated with an identification rate of 100% regardless of high BMI. Preoperative admission and preparation for surgery are streamlined by avoiding the need for wire localization and radioisotope injection.
